GUM ROSIN
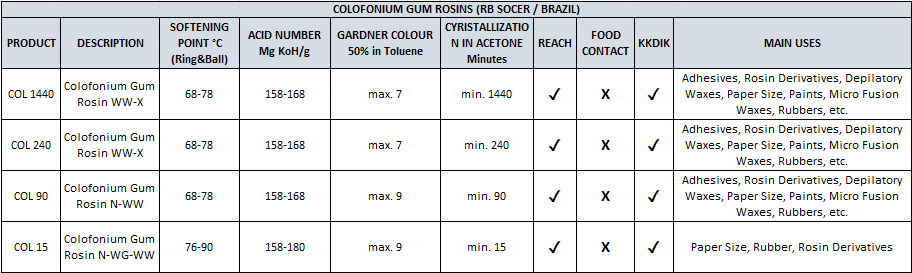
CAS number: 8050-09-7
EC NO.: 232-475-7
Molecular formula: C19H29COOH
Kimyasal yapısı:
Colophon Resin (Gum Rosin)
Colophon is the non-volatile part of the resin obtained from coniferous trees, especially pine trees. When it is called a colophone; usually a colophone obtained from a flowing resin comes to mind, but actually this term also covers the obtained colophone. For this reason, in a more general and inclusive expression; it is also called “rosin” in the literature.According to the Index of Cosmetic Ingredients (INCI), the name of the colophon is used in the cosmetic industry as “colophonium”.
Since Decolon is obtained from a natural source, its composition may differ depending on both the source from which it was obtained and the production technique, but the main components are the same, although there are proportional differences in chemical composition between different types of resins.
Colophon Resin (Gum Rosin) is a solid form of resin obtained from pine and some other plants, mostly conifers, in which volatile terpene components evaporate by heating fresh liquid resin. It is translucent and has colors ranging from yellow to black. At room temperature, colophonium is brittle, but melts with heat. It mainly contains various resin acids, especially abietic acid.
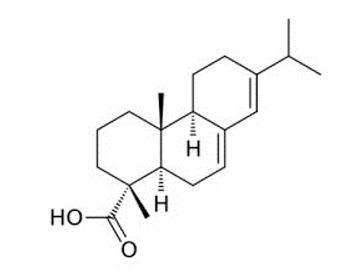
Natural resin is mainly composed of two parts, colophon and turpentine. In order to separate these components from each other, it is necessary to undergo distillation. The volatile part gets the name turpentine and contains terpenes in its structure. The solid part that remains after distillation and contains resin acids is called colophane. It is translucent and has colors ranging from yellow to black.
Resin components have variable chemical composition ratios depending on the production technique and distillation process, and the resin acids and amounts contained in them are also different. This difference constitutes the price and competitive elements in the market.
In general; resins obtained, color degree, acid number, saponification number, etc. they are characterized by quality characteristics such as.
It is known that an average of 70% of the yield resin is colophane. The composition of colophon consists of about 90% resin acids and 10% neutral substances or fatty acids.
The unmodified colophon contains oxidized material in varying amounts depending on the degree of oxidation of abietic acid, which is known to oxidize when exposed to air. It has been shown that the oxidation of abietic acid proceeds through a free radical chain reaction.
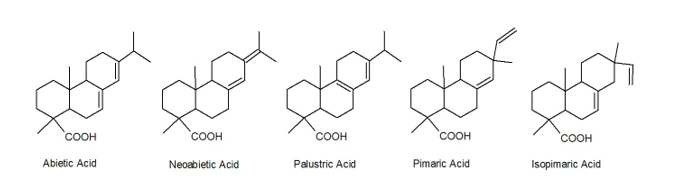
The colophon has been greatly modified for industrial use. The main component, abietic acid and its isomers, form the basis for rosin modifications and derivatives made to improve the technical properties of colophon.
Abietic acid contains two reactive sites; the first is the carboxylic acid group and the second are conjugated double bonds. All of the colophon derivatives are caused by chemical reactions in one or both of these domains. The reactions on the carboxylic acid group are esterification and salt formation and are very important commercially. Among the most important modifications related to the reactions taking place over conjugated double bonds are hydrogenation, Diels-Alder type reactions, Decertification / polymerization and formaldehyde polymerization reactions.
Resin components have variable chemical composition ratios depending on the production technique and distillation process, and the resin acids and amounts contained in them are also different. This difference constitutes the price and competitive elements in the market.
Most resins are used in a chemically modified form, not in the raw form from which they are obtained. It consists mainly of a mixture of acids of the abietic type and pimaric type, and contains a smaller amount of neutral compounds. This inherent acidity, combined with other chemical properties, allows it to be converted into a number of types used in many different applications. Derivatives include salts, esters, maleic anhydride adducts, hydrogenated, Decapitated and polymerized resins. Its most important uses include adhesives, paper sizing agents, printing inks, solders and flowables, various surface coatings, insulating materials for the electronics industry, synthetic rubber, Decoctions and soaps, and detergents. Gum Rosin is also used to prevent slipping on violin bows and strings of other stringed instruments, on dancers' shoes, and on studio and stage floors.

GUM ROSIN frequently asked questions
Colophon resin(gum rosin) is used in industrial adhesive production, cosmetic-wax production( sir wax), rubber and tire industry, paint industry.
The melting degree of colophon resins(gum rosin) is usually in the range of 68-90 °C.
There are 2 types of packaging, bagged and barrel.
1 barrel of colophon resin(gum rosin) is 250 kg.
Bagged colophon resin (gum rosin) is in 25 KG kraft paper bags.

